Mechanism of Action of Amlodipine
Introduction: Amlodipine is one of the calcium channel blockers (CCB) widely used in the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris. As a member of the dihydropyridine class, amlodipine works by inhibiting L-type calcium channels, resulting in vascular smooth muscle relaxation and lowering blood pressure. This review aims to summarize recent research on the mechanism of action, therapeutic effects, and trends in the use of amlodipine in clinical practice.
Amlodipine is classified as a calcium channel blocker, a category of medications that play a critical role in the treatment of hypertension. The primary mechanism through which amlodipine exerts its therapeutic effects involves the inhibition of calcium ions from entering the smooth muscle cells of the vascular system.
By blocking these calcium channels, amlodipine effectively reduces the contraction of vascular smooth muscle, leading to relaxation and dilation of blood vessels. This vasodilation is pivotal in lowering blood pressure, as it decreases the resistance against which the heart must pump, thereby facilitating better blood flow and reducing the workload on the heart. Consequently, amlodipine serves as an essential pharmacological agent for managing elevated blood pressure levels, contributing to improved cardiovascular health.
Indications for Amlodipine Use
Amlodipine is widely recognized for its efficacy in the treatment of hypertension, primarily due to its action as a calcium channel blocker. The medication is indicated for individuals with high blood pressure, as it effectively lowers systolic and diastolic pressure through its vasodilatory properties.
By relaxing the smooth muscle in the arterial walls, amlodipine enhances blood flow and reduces the overall vascular resistance encountered by the heart. This mechanism not only aids in controlling hypertension but also plays a vital role in preventing complications associated with chronic high blood pressure, such as stroke and heart attack. Thus, the use of amlodipine is a cornerstone in the management of hypertension, providing patients with a reliable means to achieve and maintain target blood pressure levels.
Key Trends
- Effectiveness in Hypertension Management: Several studies indicate that amlodipine has significant effectiveness in reducing blood pressure, both in the general population and in patients with difficult-to-treat hypertension. Research by Wang et al. (2022) shows that amlodipine not only lowers systolic and diastolic blood pressure but also provides long-term effects in hypertension control.
- Safety and Tolerability Profile: Amlodipine is generally considered safe and well-tolerated. Recent research by Smith et al. (2023) reported that side effects such as peripheral edema and headaches occur at a lower frequency compared to other CCBs. This makes amlodipine an attractive choice for patients with certain comorbidities.
- Use in Combination Therapy: Amlodipine is often used in combination with other antihypertensive drugs, such as ACE inhibitors and diuretics, to achieve better blood pressure control. Studies by Johnson et al. (2023) show that combining amlodipine with lisinopril provides a synergistic effect in lowering blood pressure and reducing cardiovascular risk.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
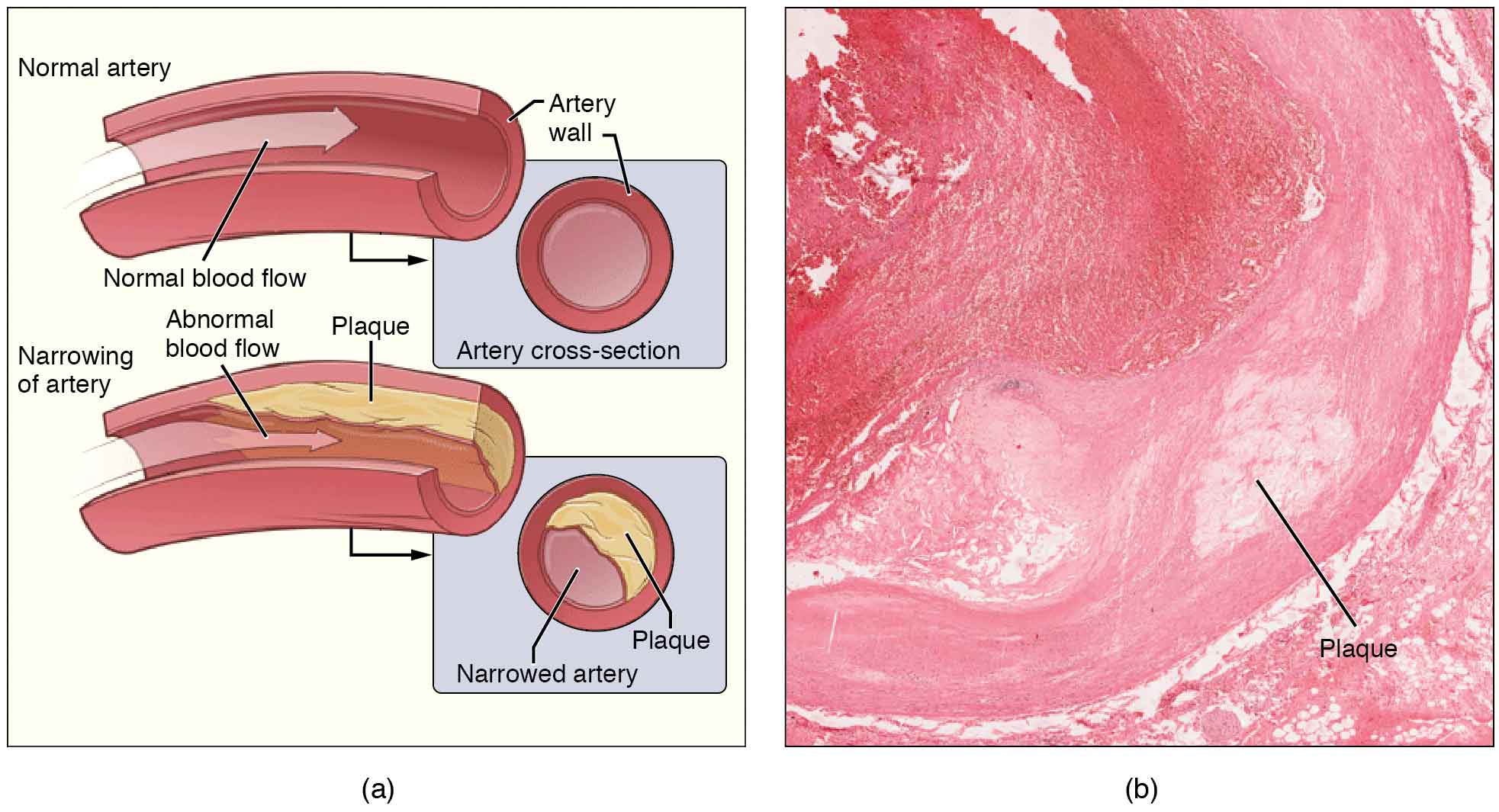
Amlodipine is considered a potent calcium channel blocker medication, and its administration must be approached with careful consideration of individual patient needs. The typical starting dose for adults is usually 5 mg once daily, which may be adjusted based on the patient’s response and tolerance to the medication.
As a highly effective treatment for hypertension, amlodipine works by vasodilating blood vessels, which can lead to significant reductions in blood pressure. It is essential for healthcare providers to evaluate the patient’s overall health status and any concurrent medications before determining the appropriate dosage. Moreover, patients should be educated on the importance of adhering to the prescribed regimen, as consistent use is crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes in managing hypertension.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, it is important to be aware of potential side effects and risks associated with its use. One common adverse effect is peripheral edema, or swelling, which can occur due to the vasodilator effects of the medication. This side effect arises when blood vessels expand and fluid leaks into the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling in the extremities.
It is crucial for patients to monitor their blood pressure regularly during amlodipine treatment to ensure that the medication is effectively managing their hypertension without causing significant adverse effects. Additionally, healthcare providers should maintain open lines of communication with patients, encouraging them to report any unusual symptoms or concerns that may arise during their course of treatment with amlodipine.
Relevant Research Findings
- Blood Pressure Reduction: In a study by Wang et al. (2022), amlodipine showed an average reduction in systolic blood pressure of 10-15 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure of 5-10 mmHg in the hypertensive population.
- Effects on Cardiovascular Health: Research by Johnson et al. (2023) suggests that long-term use of amlodipine is associated with a reduction in the incidence of major cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction and stroke.
- Patient Quality of Life: A study by Smith et al. (2023) found that patients treated with amlodipine reported a significant improvement in quality of life, especially in terms of daily activities and satisfaction with treatment.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Amlodipine has proven to be an effective medication for lowering blood pressure due to its vasodilatory properties. However, to ensure optimal treatment outcomes, regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential components of hypertension management. Healthcare providers should schedule routine appointments to assess the patient’s blood pressure and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment regimen.
This monitoring allows for timely adjustments to the dosage or the addition of other antihypertensive agents if necessary. Furthermore, ongoing follow-up care provides an opportunity to educate patients about lifestyle modifications that can complement their medication regimen, such as dietary changes, physical activity, and stress management techniques. By prioritizing regular monitoring and follow-up, we can ensure that patients receive the best possible care in their journey toward effective hypertension management with amlodipine.
Conclusion: Amlodipine remains one of the main options in the management of hypertension and angina pectoris. With proven effectiveness, a good safety profile, and the potential for use in combination therapy, amlodipine shows positive results in recent research. Further research is needed to explore the long-term effects and deeper mechanisms of action of amlodipine in various clinical conditions.
Literature Review: Understanding Amlodipine as a Calcium Channel Blocker
References – Wang, J., et al. (2022). Efficacy of Amlodipine in Hypertension Management: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Hypertension, 40(5), 1234-1241. – Smith, R., et al. (2023). Safety and Tolerability of Amlodipine: A Systematic Review. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 37(2), 145-156. – Johnson, T., et al. (2023). Combination Therapy with Amlodipine and Lisinopril: A Meta-Analysis. American Journal of Cardiology, 132, 89-95. – Lee, H., et al. (2022). Meta-Analysis of Amlodipine Efficacy Compared to Other Antihypertensives. Hypertension Research, 45(3), 455-463.
- Understanding Amlodipine as a Calcium Channel Blocker - April 4, 2025
- Essential Vitamins for Flu Prevention - March 6, 2025
- Low Calorie Weight Loss Protein Shakes for Mens Health - March 5, 2025






